Network Readiness Guide
This guide helps you evaluate and prepare your network for cloud-based VoIP services by defining key components, protocols, and configuration best practices.
Key Network Components
Section titled “Key Network Components”- ISP & Modem: Your Internet connection (fiber, cable, DSL) terminates at a modem. When using a separate router/firewall, set the modem to Bridge Mode to avoid double NAT.
- Router: Routes traffic between WAN and LAN. Configure static or dynamic routes appropriately.
- Switch: Layer 2 aggregation devices for LAN connectivity; use VLANs to segment traffic if needed.
- Bridge Mode: Puts a combo modem/router into modem-only mode, disabling its DHCP and NAT functions.
VoIP Protocols
Section titled “VoIP Protocols”- SIP (Port 5060/UDP): Handles call setup and teardown. Prioritize SIP traffic in your firewall/QoS rules.
- RTP (Ports 10000–20000/UDP): Carries voice media. Reserve these ports for call audio.
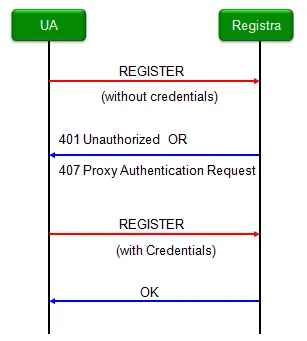
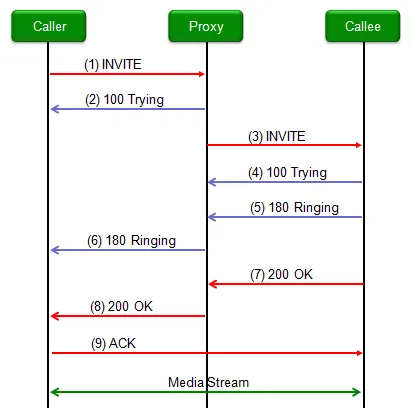
How VoIP Works
Section titled “How VoIP Works”- Registration: Devices register via SIP to the cloud to maintain reachability.
- Call Setup: SIP messages negotiate media ports (RTP).
- Media Exchange: RTP streams voice data once the call is active.
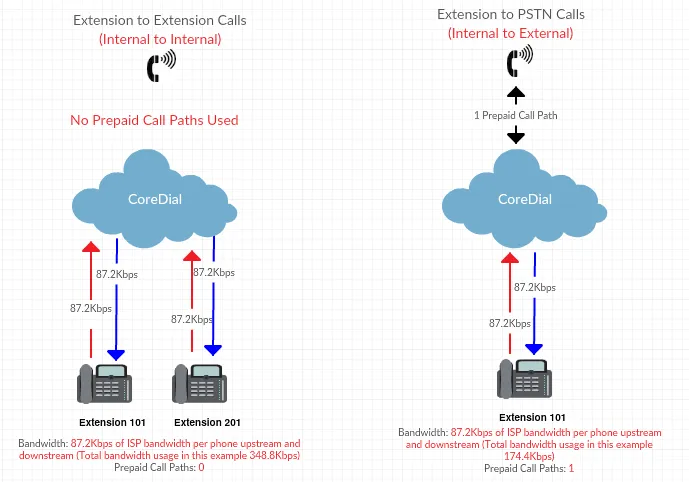
Bandwidth & Call Paths
Section titled “Bandwidth & Call Paths”- G.711 Codec: ~87.2 kbps each direction per call. Use this to calculate needed upstream/downstream capacity.
- Call Paths: Only calls to/from the PSTN consume prepaid call paths; internal calls within the cloud do not.
Performance Metrics
Section titled “Performance Metrics”- Packet Loss: Aim for ≤0.75%.
- Jitter: ≤50 ms.
- Latency: ≤150 ms.
- MOS: ≥3.6 for acceptable call quality.
Recommended QoS Settings:
- Enable QoS, prioritize UDP 5060 (SIP) and 10000–20000 (RTP).
- Disable SIP ALG on routers.
Network Separation Strategies
Section titled “Network Separation Strategies”-
Physical Separation: Dedicated voice and data networks with separate ISP links.
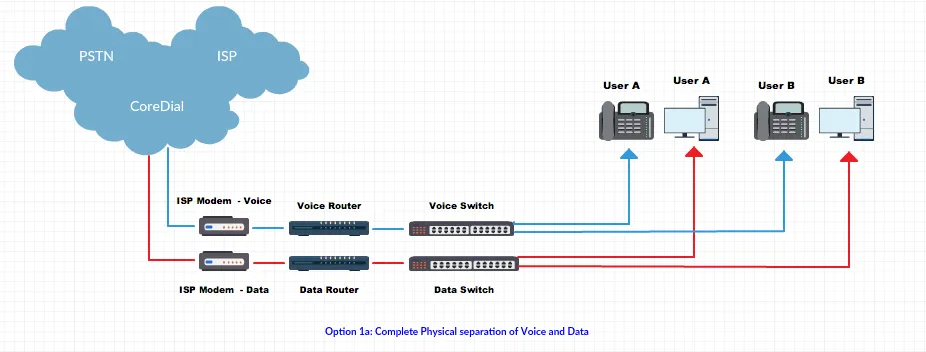
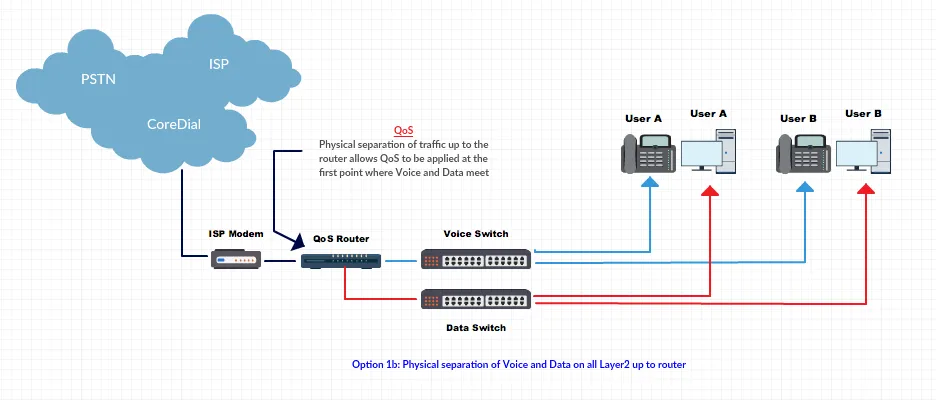
-
Logical Separation: Single LAN with VLANs for voice/data. Dual ISP or single ISP with VLAN tagging.
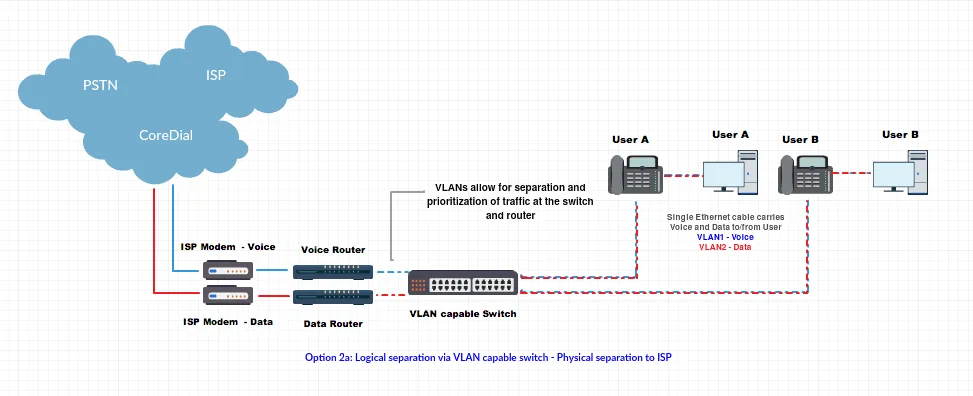
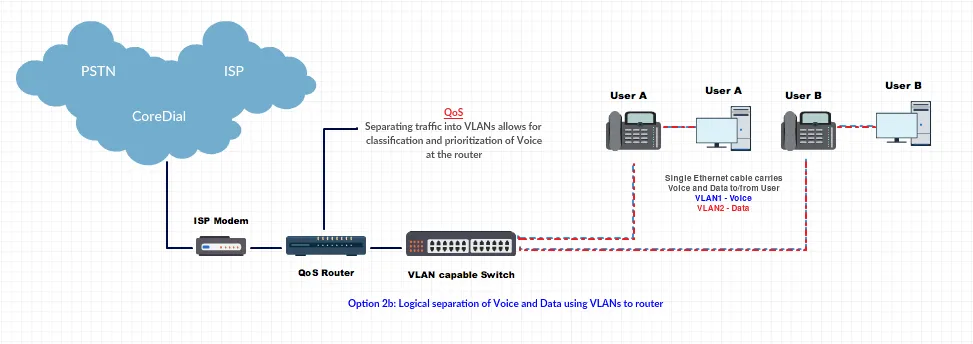
-
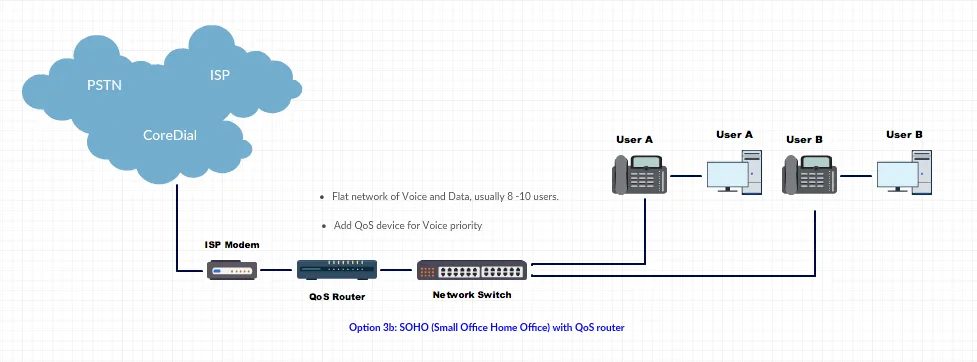
Flat SOHO Networks: Use QoS router; right-size ISP bandwidth.
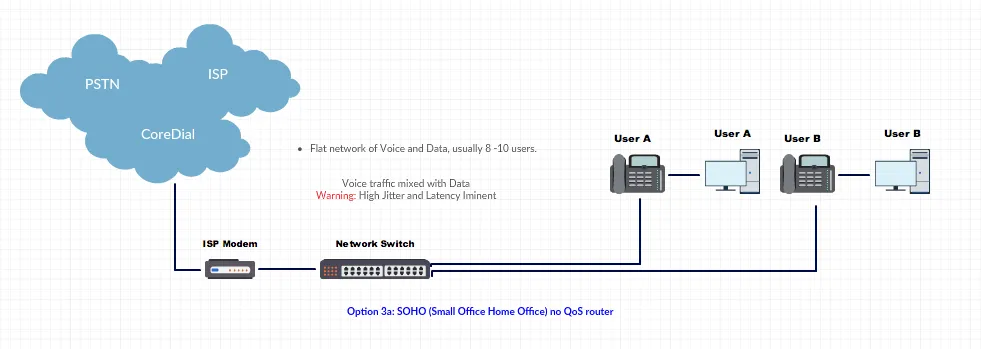
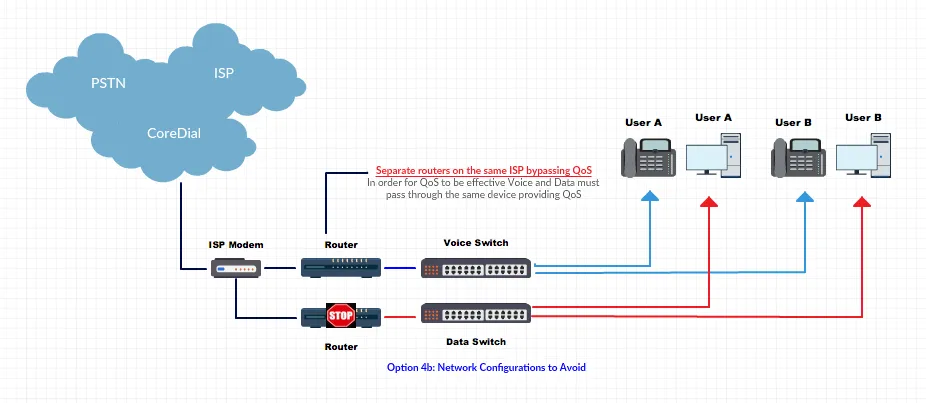
Configurations to Avoid
Section titled “Configurations to Avoid”Avoid multiple NAT devices or chained routers. Always use switches for additional LAN ports, and ensure a single NAT boundary.

Troubleshooting Tips
Section titled “Troubleshooting Tips”- Check SIP Registration: Verify device status via phone UI or PBX portal.
- Confirm Reachability: Look for offline indicators in the SIP peer status.
- Validate Network Config: Ensure single NAT, correct QoS, and bridge mode on modems.
- Isolation Testing: Move a device to a known-good network to isolate issues.